What is PVD Plating Jewelry? The Ultimate Guide (2026)

The Revolution of PVD Plating: Why Your Jewelry is About to Get a Whole Lot Tougher
In the world of fashion and fine jewelry, durability and longevity are the new luxury. Consumers are no longer satisfied with pieces that tarnish after a few wears or turn their skin green. They demand jewelry that can keep up with their active lives—jewelry that is truly waterproof and tarnish-resistant.

This demand has driven a quiet revolution in manufacturing, led by a high-tech process called PVD Plating Jewelry (Physical Vapor Deposition).
PVD is not just another way to color metal; it is a molecular bonding process that creates a coating so hard and durable it is used in aerospace and medical devices. When applied to jewelry, it transforms a beautiful piece into a long-lasting investment.
This ultimate guide will take you deep inside the PVD process, comparing it to traditional methods, explaining the science behind its superior durability, and revealing why it is the gold standard for modern jewelry brands and manufacturers like Dongguan HonHo Jewelry.
1. The Science Behind the Shine: How PVD Works
To understand why PVD Plating Jewelry is superior, you must first understand the science. PVD is a vacuum coating technique that deposits a thin film of material onto a substrate (the jewelry piece) in a highly controlled environment.
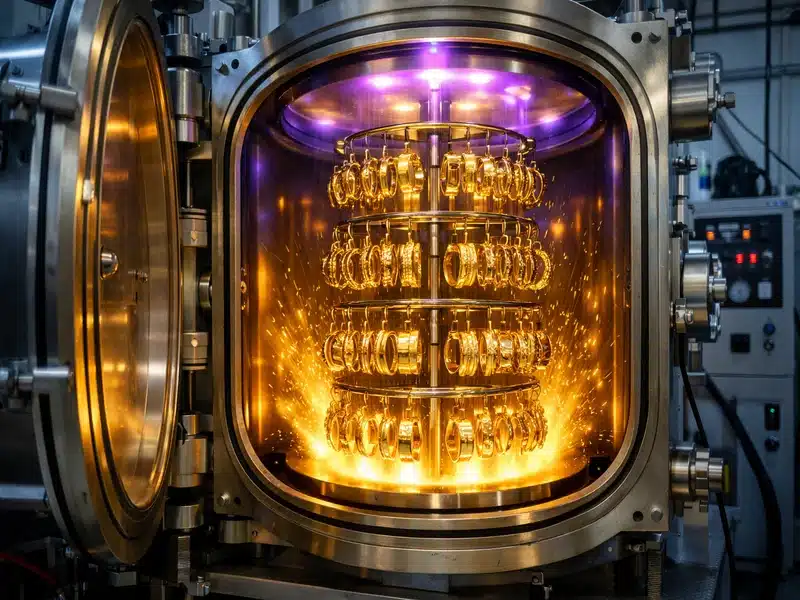
The Four Stages of Molecular Bonding
The process is complex, but it can be broken down into four critical stages that occur inside a sealed vacuum chamber:
- Preparation (The Clean Slate): The jewelry must be meticulously cleaned. Any trace of oil, dust, or even a fingerprint will compromise the bond. Manufacturers use multi-stage ultrasonic cleaning and steam cleaning to ensure the surface is atomically clean.
- Vaporization (Turning Solid into Gas): The coating material (e.g., real gold, titanium, or chromium) is heated or bombarded with ions until it vaporizes into a plasma state. This vapor is composed of individual atoms and molecules.
- Transportation (The Vacuum Highway): The vacuum chamber is crucial here. By removing all air, the vaporized atoms can travel directly to the jewelry piece without colliding with other gas molecules.
- Deposition and Bonding (The Molecular Weld): The vaporized atoms condense onto the jewelry surface, forming a thin, solid film. Crucially, the process uses an electrical charge to accelerate the ions, causing them to strike the surface with high energy. This impact creates a molecular bond—a “weld”—between the coating and the base metal, rather than just a superficial layer.
Content Gap Insight: Cathodic Arc vs. Sputtering
There are two primary methods for PVD: Magnetron Sputtering and Cathodic Arc Evaporation. While both are PVD, the latter, often used by high-end manufacturers, uses an electric arc to vaporize the target material. This method is known for producing coatings with superior adhesion and density, which translates directly to enhanced durability and a more vibrant finish on the final PVD Plating Jewelry piece.
2. PVD vs. Traditional Electroplating: The Showdown
For decades, electroplating was the industry standard. However, PVD has emerged as the clear winner in almost every metric, especially for fashion jewelry that needs to withstand daily wear.
The key difference lies in the bond. Electroplating is a chemical process that creates a weak, porous layer, while PVD is a physical process that creates a dense, molecularly bonded layer.
| Feature | PVD Plating Jewelry | Traditional Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Bonding Method | Physical Vapor Deposition (Molecular Weld) | Electrochemical Reaction (Superficial Layer) |
| Durability | Superior. Highly resistant to abrasion and corrosion. | Fair. Prone to scratching and flaking. |
| Thickness | Typically 0.03 to 0.1 microns. | Typically 0.03 to 0.1 microns (Flash Plating). |
| Hardness (Vickers HV) | High. Often 1500-3000 HV (Titanium Nitride). | Low. Typically 100-200 HV (Soft Gold). |
| Environmental Impact | Low. Zero toxic wastewater (Eco-friendly). | High. Uses chemical baths and produces toxic sludge. |
| Longevity | Can last 2-5 years or more with proper care. | Often lasts 6-12 months before noticeable fading. |
EEAT Focus: Durability Benchmarks
The hardness of the coating is a critical technical metric. The Vickers Hardness (HV) scale measures a material’s resistance to indentation. Traditional gold is soft, measuring around 100 HV. PVD Plating Jewelry that uses a titanium nitride base layer can achieve hardness levels of 1500 HV to 3000 HV [1]. This is why PVD jewelry is so resistant to scratching and wear—it’s literally harder than most steel.
3. Why PVD Plating Jewelry is a Game-Changer for Brands
The technical superiority of PVD translates directly into major benefits for both jewelry brands and their customers.
A. True Waterproof and Tarnish-Resistance
Because the PVD coating is applied in a vacuum, the resulting film is incredibly dense and non-porous. This molecular shield prevents moisture, air, and chemicals (like perfume or sweat) from reaching the base metal. This is the secret to why PVD Plating Jewelry is genuinely waterproof and tarnish-resistant.
Manufacturers like HonHo Jewelry back this claim with rigorous testing, including the 48-hour Salt Spray Test, which simulates years of corrosive wear. Only PVD can consistently pass this benchmark.
B. Hypoallergenic and Biocompatible
Traditional electroplating often requires a nickel layer to improve adhesion, which is a common allergen. PVD, however, bonds directly to the base metal (often 316L stainless steel) without the need for a nickel underlayer.
Furthermore, the materials used in PVD (like titanium and chromium) are often biocompatible—meaning they are safe for use inside the human body. This is why PVD is used for surgical implants and dental tools, making it the ultimate standard for jewelry safety [2].
C. Superior Color Consistency and Range
PVD allows for precise control over the color and finish. By vaporizing different target materials (e.g., 18K gold, titanium, or zirconium), manufacturers can achieve a wide spectrum of colors, including:
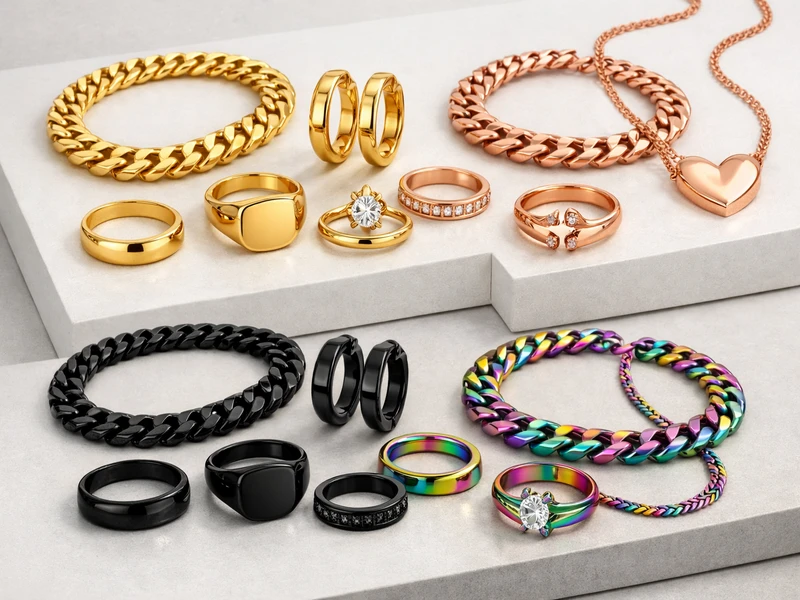

- Classic Gold: Using real 18K or 24K gold targets.
- Rose Gold: Achieved by adding copper to the gold target.
- Black/Gunmetal: Created using carbon or titanium carbide.
- Coffee/Bronze: Achieved through specific alloy mixtures.
This consistency is vital for brands that need their collections to match perfectly across different production batches.
4. Materials Matter: Why Stainless Steel + PVD is the Perfect Match
While PVD can be applied to various metals, its most powerful application is on 316L Stainless Steel. This combination creates a piece of jewelry that is virtually indestructible in daily life.
The Synergy:
- 316L Stainless Steel: This is a marine-grade steel that is already highly resistant to corrosion and tarnish. It provides an incredibly strong, stable foundation.
- PVD Coating: The PVD process creates a molecular bond with the stainless steel, enhancing its existing properties. The resulting piece is not only non-tarnishing but also highly scratch-resistant.
While PVD can be applied to brass or sterling silver, these softer base metals are more susceptible to bending and scratching, which can eventually compromise the PVD layer. The pairing of PVD with stainless steel is the ultimate choice for maximum longevity and durability. Explore our 316L Stainless Steel PVD collections here.
5. The Sustainability Factor: Eco-Friendly Jewelry Production
In an era where consumers prioritize sustainability, the environmental benefits of PVD are a significant selling point.
Traditional electroplating relies on large vats of highly toxic chemicals, including cyanide, which results in hazardous wastewater that requires complex and costly treatment before disposal.
PVD is a “Zero-Discharge” Process. Because the entire process occurs in a sealed vacuum chamber, it does not use chemical baths and produces virtually no toxic waste. The only byproducts are the solid target materials, which can often be recycled. This makes PVD a far more responsible and eco-friendly choice for jewelry manufacturing, aligning with the growing global demand for sustainable sourcing [3].
6. How to Identify High-Quality PVD Plating
Not all PVD Plating Jewelry is created equal. A high-quality manufacturer will be transparent about their process and provide verifiable data.
A. The XRF Test: Verifying Micron Thickness
The single most important factor in PVD quality is the thickness of the coating. This is measured in microns (µm).
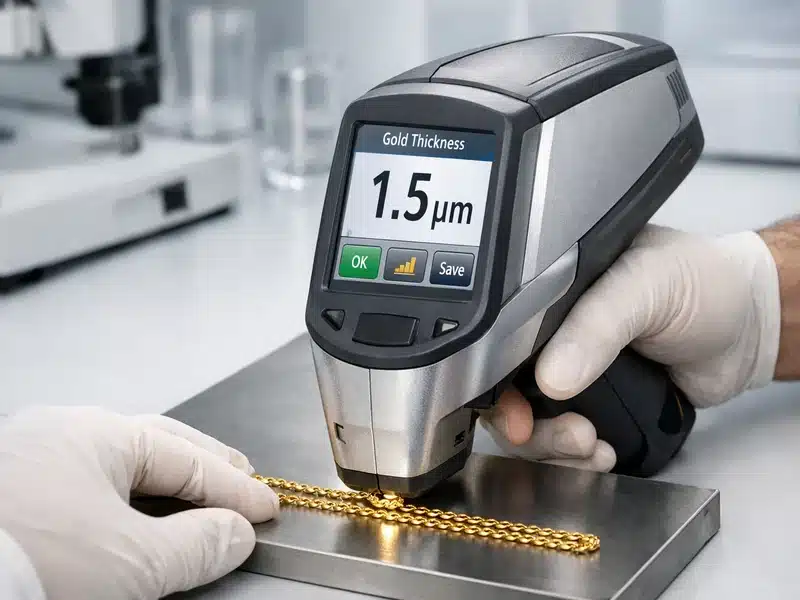

- Flash Plating: Less than 0.01 µm (Will fade quickly).
- Standard PVD: 0.03 µm to 0.5 µm (Good for daily wear).
- Premium PVD (HonHo Standard): 0.5 µm to 0.1 µm (Maximum durability, ideal for rings and bracelets).
A reputable manufacturer will use an X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) Analyzer to measure this thickness precisely. If a supplier cannot provide XRF data, their PVD claims should be viewed with skepticism.
B. The Salt Spray Test: Proving Corrosion Resistance
The salt spray test is an accelerated corrosion test that simulates years of exposure to harsh environments.
| Plating Type | Salt Spray Test Benchmark | Expected Longevity |
|---|---|---|
| Flash Electroplating | 4 – 8 hours | 6 months |
| Standard Electroplating | 12 – 24 hours | 1 year |
| Premium PVD Plating | 48 – 72 hours | 2+ years |
A PVD piece that withstands 48 hours of continuous salt spray is proven to be highly durable, making it truly waterproof and tarnish-resistant.
7. Caring for Your PVD Plated Jewelry
Despite its incredible durability, PVD jewelry still benefits from simple care to maintain its molecular bond and brilliant shine.
Maintenance Myths Debunked:
- Myth: PVD jewelry is indestructible. Reality: While highly scratch-resistant, PVD can still be damaged by sharp objects or abrasive cleaners.
- Myth: PVD jewelry never needs cleaning. Reality: Sweat, lotions, and dirt can dull the finish.
Simple Cleaning Steps:
- Warm Water and Mild Soap: Use a soft cloth or a very soft toothbrush with warm water and a mild, non-abrasive soap (like dish soap).
- Rinse and Dry: Rinse thoroughly and pat dry immediately with a soft, lint-free cloth. Do not air dry, as water spots can form.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Never use jewelry cleaners containing ammonia, alcohol, or bleach, as these can attack the base metal or the PVD bond over time.
8. Why Choose Dongguan HonHo Jewelry for PVD Manufacturing
For brands seeking a reliable partner, the choice of manufacturer is as important as the choice of plating technology. HonHo Jewelry stands out as a leader in PVD Plating Jewelry manufacturing in Dongguan.
Our commitment to quality is built on vertical integration: we operate our own in-house PVD vacuum plating plant. This means we control the entire process—from the initial cleaning to the final molecular bond—ensuring the highest quality and consistency for every piece. This control allows us to offer a 24-month plating warranty on our PVD pieces, a guarantee few in the industry can match. Learn more about our in-house PVD services .
Ready to elevate your brand with the ultimate in jewelry durability and quality?
Contact HonHo Jewelry Today to Discuss Your Custom Design Inquiry
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is PVD plating real gold?
PVD Plating Jewelry can use real gold. The process involves vaporizing a target material, which can be 18K or 24K gold, and bonding those gold atoms to the base metal. The final product contains a layer of real gold, but it is not solid gold. This method provides the look and feel of gold with vastly superior durability.
2. Can I wear PVD jewelry in the shower?
Yes, you can. PVD Plating is highly resistant to water and corrosion because of its dense, non-porous molecular bond. Unlike traditional electroplating, which can quickly degrade when exposed to moisture, PVD is designed to be waterproof and can be worn while showering, swimming, or exercising.
3. Does PVD plating fade over time?
All plating will eventually show wear, but PVD plating fades significantly slower than traditional methods. Due to the molecular bond and superior hardness, high-quality PVD plating (1.0 µm or thicker) can last for several years before any noticeable change, especially when applied to durable base metals like stainless steel.
4. Is PVD coating hypoallergenic?
Yes, PVD coating is generally considered hypoallergenic. It does not require the use of nickel as an underlayer, and the final coating materials (like titanium nitride) are often biocompatible, making them safe for sensitive skin.
5. How thick is PVD plating on jewelry?
The thickness of PVD plating for premium jewelry typically ranges from 0.03 microns (µm) to 0.1 microns (µm). For comparison, standard flash electroplating is often less than 0.1 µm. The thicker the PVD layer, the longer the piece will last.
6. What is the difference between IP plating and PVD plating?
IP (Ion Plating) is a specific type of PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition). IP is an older term often used to describe the process where ions are accelerated to enhance the bond. Essentially, all IP is PVD, but PVD is the broader, more modern term encompassing advanced techniques like Magnetron Sputtering.
7. Why is PVD jewelry more expensive than electroplated jewelry?
PVD jewelry is more expensive due to the high cost of the specialized equipment (vacuum chambers, XRF analyzers) and the technical expertise required to operate the process. The superior durability and longevity, however, make it a better long-term investment for both brands and consumers.
8. How long does PVD jewelry last?
With proper care, high-quality PVD Plating Jewelry on a stainless steel base can last 2 to 5 years or more without significant fading or tarnishing. This is up to 10 times longer than standard electroplated jewelry.
9. Can PVD be applied to any metal?
PVD can be applied to many metals, including stainless steel, titanium, brass, and sterling silver. However, it works best on metals that can withstand the high temperatures of the vacuum process and have a stable surface, which is why 316L stainless steel is the preferred base metal.
10. Where can I find high-quality PVD Plating Jewelry?
You should look for manufacturers with in-house PVD facilities and verifiable quality control. HonHo Jewelry specializes in custom PVD Plating Jewelry using stainless steel, brass, and silver, offering superior durability and a 24-month warranty. View our latest PVD collections.
References
[1] Northeast Coating Technologies. PVD vs. Electroplating. https://www.northeastcoating.com/pvd/pvd-vs-electroplating
[2] Meideya Jewelry. What Is PVD Coating and Is It Hypoallergenic. https://meideyajewelry.com/blogs/stainless-steel-jewelry/what-is-pvd-coating-a-guide-to-durable-hypoallergenic-gold-jewelry
[3] FHR Anlagenbau GmbH. Fine PVD coatings for jewelry and decoration. https://www.fhr.biz/en/industries/decoration-jewelry
[4] Custom Fashion Jewels. The Innovative World of PVD Jewelry Plating. https://www.customfashionjewels.com/the-innovative-world-of-pvd-jewelry-plating/
[5] HonHo Jewelry. About Us. https://www.honhojewelry.com/about/
share this recipe:
Still hungry? Here’s more

Top 50 Jewelry Brands Worth to Buy 2026: The Definitive Investment & Style Encyclopedia
The global jewelry market in 2026 is a fascinating landscape where centuries-old heritage meets cutting-edge

Why Brass Jewelry Wholesale Fits Fashion Brands: The Strategic Guide for 2026
In the rapidly evolving landscape of the global fashion industry, the demand for affordable luxury

Enamel Jewelry Wholesale: Adding Color to Your Brand’s Collections
In the ever-evolving world of fashion, color has become the ultimate tool for self-expression. For
Ready to Design Your Own Jewelry?
Have an idea in mind or need help shaping it? From sketches to finished pieces, our custom jewelry team will work with you step-by-step to bring your vision to life.
